THE LOGISTICAL EFFICIENCY OF THE RAILWAY NETWORK - BRAZIL X USA
Introduction
With the process of globalization, nations worldwide are experiencing an increase in international trade. In this context, Brazil has been making constant efforts to establish itself among the world's leading powers. In this regard, the Port of Santos plays a crucial role in the country's development, both domestically and internationally, in the eyes of global powers.
The Port of Santos is the largest port complex in Latin America and handles nearly one-third of Brazil's trade exchanges, meaning that one out of every three shipments passes through Santos. Despite its immense importance, the port faces logistical transportation issues. According to Nazário (in Flury et al., 2000:126), transportation accounts for, on average, about 60% of logistical expenses, resulting in costs that, in the case of the Port of Santos, are not being efficiently utilized.
Even with various improvement processes in place, the port has serious issues in the outflow of products such as soybeans and sugar, which end up interfering with urban traffic in the city and surrounding areas. With the increase in grain exports, the port should enhance its infrastructure, but this is not happening, leading to numerous problems, including impacts on the roads of the Baixada Santista region.
This article will be important for understanding the aforementioned problem and providing readers with ideas for its improvement and implementation. The methodology will involve research in local newspapers, adopting a qualitative and descriptive approach.
Problem Statement
Due to poor road infrastructure, road, river, and rail transport networks experience significant saturation. According to CODESP, out of every 10 tons, 4 cargo shipments related to harvests arrive in Santos by truck, resulting in 65 km-long queues—solely for soybean shipments. This is despite the fact that rail transport is cheaper for soybeans and yet only 25% of its capacity is utilized. This inefficiency disrupts urban traffic, roads, and even maritime crossings.
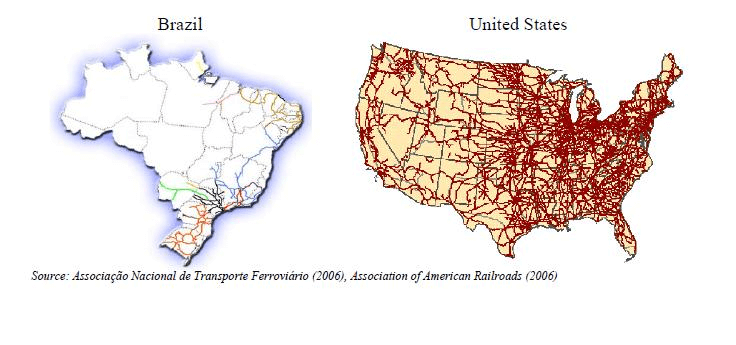
Both countries (Brazil and the U.S.) rank in the top 5 largest countries in the world by territorial size, according to data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). Brazil spans 8,514,876 km², ranking fifth on the list, while the United States covers 9,363,520 km², making it the fourth-largest country in the world. The top three are: 1st – Russia (17,075,400 km²), 2nd – Canada (9,976,139 km²), and 3rd – China (9,596,961 km²).
Justification
Based on the identified problem, the need for greater investment in railways in the country became evident. Looking solely at the raw data on territorial size and population of these two vast nations, one might assume that their railway sectors are proportionally similar—whether in terms of track mileage, maintenance of rails and trains, investments made, or any other aspect of this crucial cargo and passenger transport sector.
Objective
This article aims to conduct research on the Port of Santos, which still suffers from poor infrastructure in transportation and storage of goods and cargo. By highlighting the aforementioned problems, it encourages reflection and informs readers about the poor planning of terminals, which causes major traffic disruptions. These issues affect not only the population of the Baixada Santista but also other countries through maritime navigation.
Methodology
The research was conducted using a qualitative method, employing techniques to gather relevant data on the topic. To support the study, a bibliographic review was carried out, focusing on the concepts of infrastructure and grain harvests.
After data collection, the information was discussed in a group, questioned, and evaluated to identify key needs. Each participant sought to engage deeply with the topic, given that they are directly affected by the problem being examined.
Thus, it was possible to identify the main factors contributing to the current inefficiencies and to work on questioning and analyzing potential improvements.
Conclusion/Final Considerations Palavras-chave: Logística. Malha. Investimetno. Ferroviária.
The research confirmed that the problem in question has an impact not only on the Baixada Santista region but also on international trade, as truck congestion and delays generate additional costs and setbacks in the country's grain exports.
As a result, the need for greater investment in roads and transportation networks across the country became clear. Such improvements would optimize services and allow the Brazilian financial market to achieve significant progress, enhancing its competitiveness in international trade.